
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Convair Project 7969
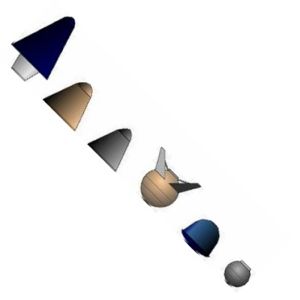 Project 7969 Designs Project 7969 ballistic designs. From left: Lockheed; Martin; Aeronutronics; Goodyear; McDonnell; Convair Credit: © Mark Wade |
Status: Study 1958. Gross mass: 450 kg (990 lb). Height: 1.52 m (4.98 ft).
6 m diameter sphere - could be launched by an Atlas within a year.
The spacecraft would be boosted by an Atlas Hustler booster into a 270 km orbit. Deorbit would be accomplished by retrorocket. The spacecraft had a ballistic coefficient (m/CdA) of 250 kg per square meter. It was expected that a first manned orbital flight could be achieved 12 months after a go-ahead.
Family: Manned spacecraft. Country: USA. Launch Vehicles: Atlas, Atlas Agena A. Agency: USAF, Convair. Bibliography: 26, 483, 59.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use