
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
ERTA
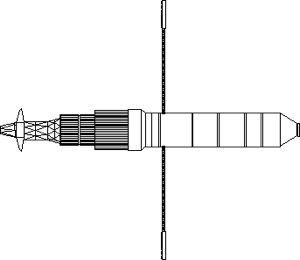 Gerkules Nuclear Tug Gerkules Nuclear Electric Interorbital Tug with 11B97 engine. Credit: © Mark Wade |
Status: Study 1992.
In the 1990's Energia studied use of nuclear electric propulsion for the scientific development project 'Mars - Nuclear electric propulsion Stage' under contract to the Russian Space Agency and the project 'Star - Soarer' under contract to the Ministry of Atomic Industry. These studies looked at designs for the 2005 period. At the beginning of the 1990's a new type of nuclear generator was studied, that would have a capacity of 150 kW in the transport role and provide 10-40 kW to power spacecraft systems while coasting. This was designated ERTA (Elecktro-Raketniy Transportniy Apparat). Technologies and concepts for this engine were studied by FEI and other organizations. A modular concept was adopted. In 1994 ERTA was studied for launch by Titan, Ariane 5, or Energia-M launch vehicles. The reactor weight was 7,500 kg and it could provide up to 10 years of electrical power traded off against 1.5 years of powered flight.
Aside from this work on the 150 kW design, there was also an examination at the same time of the use of nuclear electric propulsion for Mars expeditions. Single and multiple launch approaches were considered. For a single-launch complex of 150 metric tons a nuclear electric propulsion unit of 5 to 10 MW with enough fuel for 1.5 years would be required. For the multiple launch design, a power of 1 to 1.5 MW and fuel for three years would be required.
Family: Mars Expeditions, Space Tugs. Country: Russia. Launch Vehicles: Titan, Mars tactical rocket, Energia, Ariane. Agency: Korolev bureau. Bibliography: 89.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use