
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
HS 702
 ViaSat 2 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
Status: Operational 1999. First Launch: 1999-03-28. Last Launch: 2015-10-02. Number: 38 . Gross mass: 5,200 kg (11,400 lb).
After the payload was tailored to customer specifications, the payload module mounted to the common bus module at only four locations and with only six electrical connectors. This design simplicity conferred major advantages. First, non-recurring program costs were reduced, because the bus did not need to be changed for every payload, and payloads could be freely tailored without affecting the bus. Second, the design permitted significantly faster parallel bus and payload processing. This led to the third advantage: a short production schedule.
Further efficiency derived from the HS 702's xenon ion propulsion system (XIPS), which Hughes pioneered. XIPS was 10 times more efficient than the conventional liquid fuel systems. Four 25-cm thrusters provided economical station-keeping, needing only 5 kg of fuel per year. Using XIPS for final orbit insertion conserved even more mass. Customers could apply the weight savings to substantially increase the revenue-generating payload at small marginal cost, to prolong service life, or to change to a less expensive launch vehicle (where cost was based on satellite weight).
The HS 702 also incorporated a bipropellant propulsion system, which could lift the satellite into final orbit after separation from the launch vehicle. The bipropellant system had a fuel capacity of 1750 kg. Multiple major payloads or missions could fly on the same spacecraft. Also, customers could share the 1200-kg payload capacity with other customers, reducing launch and ground station operating costs for each participant.
The spacecraft was adaptable to medium earth and geostationary orbits. Innovative modularity extended to the HS 702 power system as well. A catalogue of standard configurations offered six different solar array arrangements, with up to five panels of solar cells per wing. As a new feature on the HS 702, angled solar reflector panels along both sides of the wings formed a shallow trough and concentrated the sun's rays on the solar cells. At the end of life, the arrays generate up to 15 kW, depending on customer payload selections. The Hughes-proprietary dual-junction gallium arsenide solar cells supplied twice the power of silicon cells at end of life. The cells were developed by Spectrolab, a Hughes Electronics Corporation subsidiary. The integrated power controller, which controlled and distributed electrical power from the solar arrays to the spacecraft, was also modular so it could be matched to the required power level. Finally, for sustained power during eclipses, the nickel-hydrogen battery comprised two kinds of cells at two power ranges, available in multiple configurations of up to 60 cells distributed in four packs.
Separating the bus and payload thermal environments and substantially enlarging the heat radiators achieved a cooler, more stable thermal environment for both bus and payload. This increased unit reliability over service life. The deployable radiators used flexible heat pipes, which increased the packageable radiator area. Further thermal control occurred through passive primary rejection via heat pipes. The HS 702 could accommodate east-west mounted antennas up to 9 feet, 4 inches in diameter, as well as a generous earth-facing array. Viewed from above, the HS 702 was rectangular. This shape left more room in a circular fairing for stowing antennas than a square spacecraft would. The additional space on the east and west sides could be used for large-aperture (and hence high-gain) antennas in various configurations. This space also enabled the antennas to retain simple, reliable, single-axis deployments.
The baseline HS 702 was compatible with all available launch vehicles. These included the Atlas II family, Delta III, Ariane 4 and 5, Long March 3B, Proton, Sea Launch, and H-II. Some customer choices affect launch vehicle options. For example, selecting a maximum-power HS 702 configuration could increase spacecraft mass and height (the extra heat dissipation equipment needed makes the satellite slightly taller), dictating use of a larger launch vehicle.
Deployed length 40.9 m maximum Payload mass up to 1200 kg. Launch mass up to 5200 kg. Stowed width, including solar panels 2.0 x 3.2 m. Stowed height (bus and payload, excluding nadir antennas) 3.6 m.
The first customer for the HS 702 was Hughes Communications, Inc., which merged with PanAmSat Corporation in May 1997 to create the world's largest privately owned communications satellite company. The HS 702 was chosen for the Galaxy and PAS fleet, to expand video distribution, telephony, and data services in North and Latin America. As of March 1999, Hughes had received orders for nine of these spacecraft: three from PanAmSat Corporation, two from XM Satellite Radio, Inc., one from Telesat Canada, and three for Spaceway..
Major problems in orbit with the solar-concentrator power generation option led to abandonment of this feature in later versions of the bus.
More at: HS 702.
| Galaxy 11 Communication satellite built by Boeing for PanAmSat, USA. Launched 1999. Used the BSS-702 bus. |
| Thuraya 1 Communication satellite built by Hughes for Thuraya Satellite Telecommunications Co., UAE. Launched 2000. Used the HS-GEM (Geomobile) bus. |
| PAS 1R Communication satellite built by Hughes / Boeing for PanAmSat, USA. Launched 2000. Used the BSS-702 bus. |
| Anik F1 Communication satellite built by Boeing for Telesat Canada, Canada. Launched 2000. Used the BSS-702 bus. |
| XM 1, 2 (XM Rock, Roll) Null |
| Galaxy 3C Communication satellite built by Boeing for PanAmSat, USA. Launched 2002. Used the BSS-702 bus. |
| Thuraya 2, 3 Communication satellite built by Boeing for Thuraya Satellite Telecommunications Co., UAE. Launched 2003 - 2008. Used the BSS-GEM (Geomobile) bus. |
| Anik F2 Communication satellite built by Boeing for Telesat Canada, Canada. Launched 2004. Used the BSS-702 bus. |
| XM 3, 4 (XM Rhythm, Blues) Null |
| Spaceway Series of heavy communications satellites for DirecTV. Used the HS 702 bus. Communication satellite built by Boeing for DirecTV (#1, #2); Hughes Network Systems (#3), USA. Launched 2005 - 2007. Used the BSS-702 bus. |
| NSS 8 Communication satellite built by Boeing for SES New Skies, Netherlands. Launched 2007. Used the BSS-702 bus. |
| DirecTV 10, 11, 12 Communication satellite built by Boeing (BSS) for DirecTV, USA. Launched 2007 - 2009. Used the BSS-702 bus. |
| WGS 1, 2, 3 (WGS Block 1) Null |
| SkyTerra 1, 2 (MSV 1, 2, SA) Null |
| WGS 4, 5, 6, 7 (WGS Block 2) Null |
| Intelsat 22 Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Intelsat, USA. Launched 2012. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| Intelsat 21 Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Intelsat, USA. Launched 2012. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| Intelsat 27 Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Intelsat, USA. Launched 2013. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| Inmarsat-5 F1, 2, 3, 4 Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Inmarsat, International. Launched 2013 - 2017. Used the BSS-702HP bus. |
| ABS 3A Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Asia Broadcast Satellite (ABS), China. Launched 2015. Used the BSS-702SP bus. |
| Eutelsat 115 West B (SATMEX 7) Null |
| MEXSAT 1, 2 (Centenario, Morelos 3) Null |
| Intelsat 29e Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Intelsat, USA. Launched 2016. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| SES 9 Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for SES World Skies, USA. Launched 2016. Used the BSS-702HP bus. |
| ABS 2A (MongolSat 1) Null |
| Eutelsat 117 West B (SATMEX 9) Null |
| Intelsat 33e Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Intelsat, USA. Launched 2016. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| WGS 8, 9, 10 (WGS Block 2 Follow-On) Null |
| ABS 8 Communicationsatellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Asia Broadcast Satellite (ABS). Used the BSS-702SP bus. |
| AMOS 17 Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Spacecom Ltd., Israel. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| APMT 1, 2 Communicationsatellite built by Hughes for Asia-Pacific Mobile Telecommunications Satellite (APMT) Pte. Ltd.. Used the HS-GEM (Geomobile) bus. |
| GiSAT 1 Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Global IP, Cayman Islands. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| Horizons 3e Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Intelsat, SKY Perfect JSAT, USA. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| Intelsat 35e Communicationsatellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for Intelsat. Used the BSS-702MP bus. |
| JCSat 18 / Kacific 1 Null |
| SES 15 Communicationsatellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for SES World Skies. Used the BSS-702SP bus. |
| Silkwave 1 (NYBBSat 1) Null |
| Skyterra GeoMobile class satellite with a 22-meter L-band reflector. Used the HS 702 bus. |
| ViaSat 2 Communicationsatellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems for ViaSat Inc.. Used the BSS-702HP bus. |
| ViaSat 3 Americas, Asia, EMEA Communication satellite built by Boeing Satellite Systems (bus); ViaSat Inc. (payload) for ViaSat Inc., USA. Used the BSS-702HP bus. |
| WGS USAF Wideband Global Satcom satellite, designed to replace the DSCS series. The satellite carried X-band and Ka-band communications payloads. Used the HS 702 bus. |
Family: Communications, Geosynchronous orbit, Sea-Launched, Technology. Country: USA. Launch Vehicles: Proton, Ariane, Ariane 44L, Ariane 5, Ariane 5G, Zenit-3SL, Atlas V, Proton-M/Briz-M, Delta IV, Ariane 5ECA, Ariane 5Gp, Atlas V 421, Delta 4M+(5,4), Falcon 9 v1.1, Falcon 9. Projects: DirecTV, Galaxy, Intelsat, Thuraya. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral, Baikonur, Cape Canaveral LC17B, Cape Canaveral LC37B, Cape Canaveral LC40, Cape Canaveral LC41, Kourou, Baikonur LC200/39, Kourou ELA2, Kourou ELA3, Kiritimati. Agency: Hughes. Bibliography: 2, 296, 444, 552, 554, 12604, 12605, 12606, 12607, 12608, 12609, 12610, 12611, 12612, 12613, 12614, 12615, 12616, 12617, 12618, 12619, 12620, 12621, 12622.
 | ABS 2 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | ABS-3A Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | ABS 8 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Anik F1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Anik F2 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | APMT 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | DirecTV-10 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Galaxy 11 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Galaxy 3C Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Inmarsat 5 F1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Intelsat 29e Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Intelsat 33e Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Intelsat 35e Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Intelsat IS-21 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Intelsat IS-27 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Mexsat-1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Skyterra 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | NSS 8 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | PAS 1R Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | SES 9 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Spaceway 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
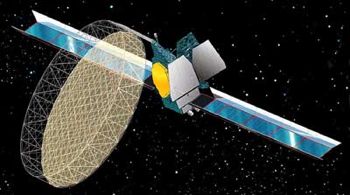 | Thuraya 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | Thuraya 2 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | USA 195 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | USA 233 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | XM-1 Roll Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | XM-3 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | DemoSat Credit: Manufacturer Image |
 | DemoSat Credit: Manufacturer Image |
1995 October - .
- Hughes announced HS 702 satellite series - . Nation: USA. Spacecraft: HS 702. Hughes Space and Communications Company announced a new satellite series, the HS 702, evolved from the HS 601 and HS 601HP (high-power)..
1999 March 28 - . 01:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- DemoSat - .
Payload: HS 702. Mass: 4,500 kg (9,900 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: SeaLaunch.
Manufacturer: Kent.
Class: Technology.
Type: Navigation technology satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 25661 . COSPAR: 1999-014A. Apogee: 36,045 km (22,397 mi). Perigee: 658 km (408 mi). Inclination: 0.70 deg. Period: 645.00 min.
The first Boeing Sea Launch mission. The Zenit-3SL lifted off from the Odyssey floating platform on the equator at 154 degrees West longitude. The DemoSat payload was an instrumented dynamic model of an HS-702 satellite built by Boeing Commercial Space/Kent. 13 minutes after launch, the Block DM-SL upper stage completed its first burn and entered a 180 km x 735 km x 1.2 degree parking orbit. A second burn 47 minutes after launch placed DemoSat in a 638 km x 36,064 km x 1.2 degree geostationary transfer orbit. Three hours later, a third DM-SL burn lowered the stage's perigee so that it would re-enter quickly.
1999 December 22 - . 00:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA2. LV Family: Ariane. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 44L.
- Galaxy 11 - .
Mass: 4,484 kg (9,885 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: PanAmSat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Galaxy.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702 .
USAF Sat Cat: 26038 . COSPAR: 1999-071A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Communications satellite. Third Ariane launch within three weeks. First Hughes HS 702 bus satellite, for PanAmSat Corporation to expand video and telecommunications services to North America and Brazil. The 20-watt C-band transponders will be used primarily for cable television customers. The Ku-band payload offers two power levels: 140 watts for video distribution, and 75 watts for data networks and other general communications services. This gives Galaxy 11 a total payload of 64 active transponders. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 99 deg W in 2000. As of 4 September 2001 located at 91.01 deg W drifting at 0.010 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 91.01W drifting at 0.008W degrees per day.
2000 October 21 - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- Thuraya 1 - .
Payload: BSS-GEM. Mass: 5,108 kg (11,261 lb). Nation: UAE.
Agency: Thuraya.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Thuraya.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 26578 . COSPAR: 2000-066A. Apogee: 35,808 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,764 km (22,222 mi). Inclination: 5.20 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Mobile Communications satellite. Launch delayed from September 18 and October 19. Stationed at 44 deg E. The first Boeing GEM satellite, Thuraya 1, was built by Boeing/El Segundo (formerly Hughes). It was based on the HS-702 design but featured a large 12-m diameter truss antenna for L-band mobile telephone service. Launch mass of Thuraya was 5108 kg; dry mass probably around 3000 kg. The satellite was to be delivered after on orbit testing to Etisalat, the Emirates Telecom Corp of Abu Dhabi, and its Thuraya Satellite subsidiary. Thuraya was launched from the Odyssey platform in the Pacific Ocean positioned on the equator at 154 deg W. The two-stage Yuzhnoe Zenit core delivered Thuraya and its Energiya Blok DM-SL upper stage to a -2212 x 182 km suborbital trajectory. The first DM-SL burn placed the stack in a 180 x 200 km x 6.3 deg parking orbit at 0604 GMT; a second burn at 0733 GMTput Thuraya in a 210 x 35891 km x 6.3 deg geostationary transfer orbit. A later depletion burn lowered the DM-SL stage perigee to 180 km, as burns by Thuraya's liquid engine raised it towards geosynchronous orbit. Positioned in geosynchronous orbit at 44 deg E in 2000. As of 5 September 2001 located at 44.22 deg E drifting at 0.003 deg E per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 98.57E drifting at 0.007W degrees per day.
2000 November 16 - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA3. LV Family: Ariane 5. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 5G.
- PAS 1R - .
Mass: 4,758 kg (10,489 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: Panamsat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Panamsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 26608 . COSPAR: 2000-072A. Apogee: 35,793 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,781 km (22,233 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
First use of the ASAP-5 piggyback payload adapter. Communications satellite, stationed at 58 deg W. PAS 1R was a large Boeing Model 702 satellite with a dry mass of about 3000 kg (launch mass 4793 kg) and a solar panel span of 45m. It carried 36 C and 48 Ku-band transponders. PAS 1R was operated by Panamsat, whose fleet included the former Hughes Galaxy system. The PAS 1R, STRV 1c/1d, and AMSAT Phase 3D satellites were placed in orbit on a single Ariane launch. The EPS stage entered geostationary transfer orbit at 0134 GMT, followed by separation of the PAS 1R main payload. As of 4 September 2001 located at 45.03 deg W drifting at 0.016 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 1 located at 45.05W drifting at 0.023W degrees per day.
2000 November 21 - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA2. LV Family: Ariane. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 44L.
- Anik F1 - .
Mass: 4,711 kg (10,385 lb). Nation: Canada.
Agency: Telesat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Anik.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 26624 . COSPAR: 2000-076A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Heaviest Ariane 4 payload ever. Anik F1 was a Telesat Canada communications satellite. The Boeing model 702 satellite had a launch mass of 4852 kg and a dry mass of 2950 kg. It carried 36 C-band and 48 Ku-band transponders. As of 3 September 2001 located at 107.30 deg W drifting at 0.006 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 107.29W drifting at 0.000W degrees per day.
2001 March 18 - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- XM-2 Rock - .
Mass: 4,666 kg (10,286 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: XM Radio.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: XM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 26724 . COSPAR: 2001-012A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
The XM Radio satellites (using Boeing 702 buses) provided digital radio entertainment broadcast to the US. The XM-2 Rock satellite was accompanied by the XM-1 Roll spacecraft launched later in 2001. A Boeing Sea Launch Zenit-3SL took off from the Odyssey floating launch platform at 154W 0 N in the Pacific. The two-stage Zenit put the Blok DM in a suborbital trajectory with a 190 km apogee; the DM first burn went to a 180 x 990 km x 1.3 deg orbit, with the second burn delivering Rock to geostationary transfer orbit. The 4.7 tonne (with fuel), 18 kW satellite carried two transmitters (3 kW each) in the S-band to relay 100 channels of digital quality music uplinked in the X-band from one or more ground stations. It was parked over 114.9 deg-W longitude. The investors include several auto manufacturers who were to be equipping the special receivers in their models. As of 4 September 2001 located at 114.98 deg W drifting at 0.001 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 115.14W drifting at 0.003W degrees per day.
2001 May 8 - . 22:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- XM-1 Roll - .
Mass: 3,703 kg (8,163 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: XM Radio.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: XM.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 26761 . COSPAR: 2001-018A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Direct Radio Broadcasting satellite. Second launch attempt following pad abort on January 8. Launch delayed from May 7. XM-1 "Roll" was launched from Sea Launch's Odyssey Launch Platform in the Pacific, on the equator at 154.0 W. Roll joined Rock, launched on March 18, to complete the XM Satellite Radio space segment. The XM-1 satellite was a Boeing Satellite Systems (El Segundo) BSS 702 with a launch mass of 4667 kg and a dry mass of about 2500 kg. It carried an R-4D liquid apogee engine and a XIPS ion station-keeping engine. The satellite's Alcatel communications payload featured an X-band receive antenna which passed digital radio broadcasts on to the two 5-meter S-band transmit antennas. It was to provide one hundred channels of digital music and entertainment to motorists in North America after parking over 85 deg-W. The XM satellites, like the three rival Sirius Radio satellites in inclined elliptical synchronous orbits, were to provide radio broadcasting to North America. The first two stages of the Zenit launch vehicle placed the Block DM-SL upper stage and payload in a 191 km apogee suborbital trajectory at 2219 GMT; the Block-DM-SL then ignited for its first burn, entering a 180 x 990 km x 1.3 deg parking orbit at 2223 GMT. The second burn at 2258 GMT accelerated the stack to a 935 x 35797 km x 1.3 deg geostationary transfer orbit. The XM-1 Roll satellite separated at 2315 GMT. As of 5 September 2001 located at 85.12 deg W drifting at 0.009 deg W per day. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 115.09W drifting at 0.002W degrees per day.
2002 June 15 - . 22:39 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- Galaxy 3C - .
Mass: 4,850 kg (10,690 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: PanAmSat.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Galaxy.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 27445 . COSPAR: 2002-030A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Launch delayed from July 2001 and May 28, June 2 and 9, 2002. The Galaxy 3C satellite was launched from the Odyssey floating launch platform at its standard 154W 0N location. The Zenit second stage and the DM third stage with payload entered a -2160 x 195 km suborbital trajectory at 2248:10. At about 2252 UTC the DM stage entered a 180 x 393 km x 0 deg parking orbit. A second burn of the DM at 2324 to 2330 UTC put Galaxy 3C in a 358 x 41440 km x 0.02 deg transfer orbit This was a record low inclination for a geostationary transfer orbit. The satellite's R-4D apogee engine was to put the Boeing BSS-702 satellite in geostationary orbit. The satellite was the first 702 model to use extra solar panels instead of the solar concentrators which ran into fogging problems on the earlier 702 flights. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 95.06W drifting at 0.007W degrees per day.
2003 June 10 - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- Thuraya 2 - . Payload: BSS-GEM. Mass: 5,177 kg (11,413 lb). Nation: UAE. Agency: Thuraya. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Program: Thuraya. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 27825 . COSPAR: 2003-026A. Apogee: 35,806 km (22,248 mi). Perigee: 35,766 km (22,223 mi). Inclination: 5.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. The Boeing 'GEM' spacecraft was a modified BSS-702 with a 12 m wide antenna for L-band mobile communications. Launch delayed from January 20, then April 4. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 43.94E drifting at 0.004E degrees per day..
2004 July 18 - . 00:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA3. LV Family: Ariane 5. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 5Gp.
- Anik F2 - . Mass: 5,950 kg (13,110 lb). Nation: Canada. Agency: Telesat. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Program: Anik. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 28378 . COSPAR: 2004-027A. Apogee: 38,333 km (23,818 mi). Perigee: 33,253 km (20,662 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,436.40 min. Delayed from May, July 9, 13, 16 and 17. Heaviest single payload to GTO to that date. As of 2007 Mar 11 located at 111.09W drifting at 0.004W degrees per day..
2005 March 1 - . 03:51 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- XM-3 - . Payload: XM Rhythm. Mass: 4,703 kg (10,368 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: XM Radio. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Program: XM. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 28626 . COSPAR: 2005-008A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Delayed from February 17, 18 and 23, 2005 due to of heavy seas. The satellite would supplement the American XM network's satellite direct-broadcast digital radio service. As of 2007 Mar 9 located at 85.14W drifting at 0.010W degrees per day..
2005 April 26 - . 07:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- Spaceway 1 - . Mass: 6,080 kg (13,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: DirecTV. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Program: DirecTV. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 28644 . COSPAR: 2005-015A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Heaviest single payload to geosynchronous transfer orbit to that date. Carried 48 high-frequency Ka-band transponders for data transmission and television broadcasting. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 102.80W drifting at 0.005W degrees per day..
2005 November 16 - . 23:46 GMT - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA3. LV Family: Ariane 5. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 5ECA.
- Spaceway 2 - .
Mass: 6,116 kg (13,483 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DirecTV.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: DirecTV.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 28903 . COSPAR: 2005-046B. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Period: 1,436.10 min.
Heaviest total commercial GTO payload to that date. Qualification flight for the Ariane 5 EC-A version. Launch delayed from June 25 due to launch vehicle problems. Spaceway 2 launch delayed from April for problems with the satellite. As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 99.24W drifting at 0.010W degrees per day.
2006 October 30 - . 23:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- XM-Blues - . Mass: 6,100 kg (13,400 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: XM Radio. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Program: XM. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 29520 . COSPAR: 2006-049A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.09 min. Adds to XM Satellite Radio's constellation of direct-broadcast radio to North America (XM Rock, Roll, and Rhythm launched earlier). As of 2007 Mar 10 located at 115.02W drifting at 0.006W degrees per day..
2007 January 30 - . 23:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL. FAILURE: First stage exploded just after ignition, damaging launch platform.. Failed Stage: 1.
- NSS 8 - .
Mass: 6,100 kg (13,400 lb). Nation: Netherlands.
Agency: New Skies.
Manufacturer: El Segundo.
Program: Intelsat.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
The platform was designed to survive such an explosion, but the flame deflector was blown off and the blast doors unhinged. The launch platform was towed back to Long Beach for repairs. The time required to repair the platform and the investigation to determine and fix the cause would certainly impact the 2007 Zenit-3SL and Zenit-2 launch schedules, probably forcing customers to be diverted to other boosters. NSS-8 was to have been placed at a 57º East orbital position to satisfy demand in the Indian Ocean region with 56 C-band and 36 Ku-band transponders. NSS-703, with an expected end-of-life in 2009, would have to continue in service until a replacement was built and launched.
2007 July 7 - . 01:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- DirecTV-10 - .
Mass: 5,893 kg (12,991 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DirecTV.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: DirecTV.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 31862 . COSPAR: 2007-032A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
First launch of a pair of satellites, DirecTV 10 and 11, that will beam HDTV programs to 500 local markets from the company's primary orbital slot at 101 degrees west longitude. Acquisition and launch cost of $300 million per satellite; one ground spare also built.
2007 August 14 - . 23:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA3. LV Family: Ariane 5. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 5ECA.
- Spaceway 3 - . Mass: 6,075 kg (13,393 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Hughes. Manufacturer: El Segundo. Program: DirecTV. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 32018 . COSPAR: 2007-036A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.0200 deg. Period: 1,436.12 min. Satellite launched for Hughes Network Systems, with a Ka-band payload for space-based internet. Mass 3655 kg dry..
2007 October 11 - . 00:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. Launch Pad: SLC41. LV Family: Atlas V. Launch Vehicle: Atlas V 421.
- USA 195 - . Payload: WGS 1. Mass: 5,987 kg (13,199 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Martin. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 32258 . COSPAR: 2007-046A. Apogee: 39,016 km (24,243 mi). Perigee: 32,586 km (20,247 mi). Inclination: 0.20 deg. Period: 1,436.80 min. First USAF Wideband Global Satcom satellite, designed to replace the DSCS series, was placed by the Atlas booster in an initial 477 km x 66,847 km x 20.1 deg geosynchronous transfer orbit. The satellite carried X-band and Ka-band communications payloads..
2008 January 15 - . 11:49 GMT - . Launch Site: Sea Launch Area. Launch Pad: KIR. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- Thuraya 3 - .
Payload: BSS-GEM. Mass: 5,173 kg (11,404 lb). Nation: UAE.
Agency: Thuraya.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: Thuraya.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 32404 . COSPAR: 2008-001A. Apogee: 35,820 km (22,250 mi). Perigee: 35,756 km (22,217 mi). Inclination: 6.20 deg. Period: 1,436.20 min.
Launch vehicle return-to-flight after on-pad explosion one year earlier damaged launch platform. The satellite was positioned at 98.5 degrees East Longitude to provide L-band and C-band mobile voice, broadband, maritime, rural telephony, and fleet management to Thuraya subscribers. Design lifetime of 12 years.
2008 March 19 - . 22:48 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Pad: 0.0 N x 154.0 W. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- DirecTV 11 - .
Mass: 5,920 kg (13,050 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: DirecTV.
Manufacturer: Boeing.
Program: DirecTV.
Class: Communications.
Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 32729 . COSPAR: 2008-013A. Apogee: 35,788 km (22,237 mi). Perigee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
Placed in orbital slot 99.2° W Longitude. In combination with DirecTV 10, the satellite would allow the parent company to direct broadcast local HDTV to 90 percent of its customers in North America. The Ka-band satellite was equipped with 28 active and 8 spare TWTAs for direct broadcast to the continental United States and Alaska; 4 active and 4 spare for broadcast to the 48 stages and Hawaii; and 55 active and 15 spares for spot transmissions. Total power was 18 kW / 16 kW at beginning/end of life. Propulsion was provided by 445 N liquid apogee engine and four XIPS 35-cm ion thrusters. Mass at launch was 6060 kg and 3700 kg after on-board propellants were consumed to place the satellite in its operational geosynchronous orbit.
2009 April 4 - . 08:34 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. Launch Pad: SLC41. LV Family: Atlas V. Launch Vehicle: Atlas V 421.
- USA 204 - . Payload: WGS 2. Mass: 5,987 kg (13,199 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Martin. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 34713 . COSPAR: 2009-017A. Apogee: 35,452 km (22,028 mi). Perigee: 35,397 km (21,994 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,417.60 min. Wideband Global Satcom; provided communications for the US Dept. of Defense Central Command (CENTCOM)..
2009 December 6 - . 01:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC37B. Launch Pad: SLC37B. LV Family: Delta IV. Launch Vehicle: Delta 4M+(5,4).
- USA 211 - . Payload: WGS 3. Mass: 5,990 kg (13,200 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: Martin. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 36108 . COSPAR: 2009-068A. Apogee: 64,827 km (40,281 mi). Perigee: 31,268 km (19,428 mi). Inclination: 0.60 deg. Period: 2,106.00 min. US Army Wideband Global Satcom, carried X-band and Ka-band communications payloads..
2009 December 29 - . 00:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- DirecTV-12 - . Mass: 5,900 kg (13,000 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: ILS. Program: DirecTV. Class: Communications. Type: Civilian communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 36131 . COSPAR: 2009-075A. Apogee: 37,150 km (23,080 mi). Perigee: 34,409 km (21,380 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,435.70 min. Direct television broadcast to United States..
2010 November 14 - . 17:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Skyterra 1 - . Payload: BSS-GEM. Mass: 5,400 kg (11,900 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 37218 . COSPAR: 2010-061A. Apogee: 35,802 km (22,246 mi). Perigee: 35,772 km (22,227 mi). Inclination: 6.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. GeoMobile class satellite with a 22-meter L-band reflector..
2012 January 20 - . 00:38 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC37B. Launch Pad: SLC37B. LV Family: Delta IV. Launch Vehicle: Delta 4M+(5,4).
- USA 233 - . Payload: WGS 4. Mass: 6,000 kg (13,200 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Military communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 38070 . COSPAR: 2012-003A. Apogee: 66,872 km (41,552 mi). Perigee: 27,959 km (17,372 mi). Inclination: 1.10 deg. Period: 2,069.50 min. Fourth Wideband Global Satcom satellite, providing high bandwidth communications for the US military. Operated by US Army Space Command, placed in an initial supersynchronous geostationary transfer orbit..
2012 March 25 - . 12:10 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Intelsat IS-22 - .
Payload: BSS-702MP. Mass: 6,200 kg (13,600 lb). Nation: Luxembourg.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 38098 . COSPAR: 2012-011A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min.
The satellite hosted an Intelsat C- and Ku-band commercial communications payload and a UHF communications payload for the Australian Defense Forces. First Proton launch to use a supersynchronous orbit to maximize use of booster propellant and conserve spacecraft fuel.
2012 August 19 - . 06:55 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL.
- Intelsat IS-21 - . Payload: BSS-702MP. Mass: 5,984 kg (13,192 lb). Nation: Europe. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 38749 . COSPAR: 2012-045A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,784 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.10 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. The IS-21 satellite replaced IS-9 and in providing western hemisphere communications satellite coverage..
2013 February 1 - . 06:56 GMT - . Launch Site: Kiritimati. Launch Platform: Odyssey. LV Family: Zenit. Launch Vehicle: Zenit-3SL. FAILURE: A first-stage hydraulic pump failure 4 seconds after launch led to shut down 20 seconds later. The vehicle, with the Intelsat communications satellite, impacted the Pacific Ocean 56 seconds after launch.. Failed Stage: 1.
- Intelsat IS-27 - . Payload: BSS-702MP. Mass: 6,241 kg (13,759 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. The lost satellite carried Ku and C band communications transponders and an Italian UHF payload..
2013 May 25 - . 00:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC37B. Launch Pad: SLC37B. LV Family: Delta IV. Launch Vehicle: Delta 4M+(5,4).
- USA 243 - . Payload: WGS 5. Mass: 5,987 kg (13,199 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 39168 . COSPAR: 2013-024A. Apogee: 40,362 km (25,079 mi). Perigee: 31,171 km (19,368 mi). Inclination: 0.23 deg. Period: 1,435.07 min. Wideband Gapfiller Satellite; provided communications for the US military from geosynchronous orbit..
2013 August 8 - . 00:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC17B. Launch Pad: SLC37B. LV Family: Delta IV. Launch Vehicle: Delta 4M+(5,4).
- USA 244 - . Payload: WGS 6. Mass: 6,000 kg (13,200 lb). Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 39222 . COSPAR: 2013-041A. Apogee: 66,680 km (41,430 mi). Perigee: 20,934 km (13,007 mi). Inclination: 2.76 deg. Period: 1,864.76 min. US military X/Ka-band Wideband Global Satcom communications satellite. Funded by Australia; the Australian Defense Force also makes use of the WGS network..
2013 December 8 - . 12:12 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Inmarsat 5 F1 - . Payload: BSS-702HP. Mass: 6,090 kg (13,420 lb). Nation: International. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 39476 . COSPAR: 2013-073A. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.08 min. First Inmarsat 5 satellite, carrying the Ka-band Global Xpress communications payload.
2015 February 1 - . 12:31 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Inmarsat 5 F2 - . Payload: Boeing 702HP. Mass: 6,070 kg (13,380 lb). Nation: International. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 40384 . COSPAR: 2015-005A. Apogee: 35,789 km (22,238 mi). Perigee: 35,785 km (22,235 mi). Inclination: 0.0200 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Second satellite in the Inmarsat 5 series; launched into a supersynchronous geotransfer orbit. The satellite provided additional Ka-band mobile broadband capacity for Inmarsat Global..
2015 March 2 - . 03:50 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: Cape Canaveral SLC40. LV Family: Falcon. Launch Vehicle: Falcon 9 v1.1.
- ABS-3A - .
Payload: BSS-702SP. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: China.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 40424 . COSPAR: 2015-010A. Apogee: 35,795 km (22,241 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0100 deg. Period: 1,436.12 min.
Dual communications satellite payload placed initially in a supersynchronous transfer orbit. Falcon 9 reached a 174 km x 953 km parking orbit 9 minutes after launch, and then made a second burn over the equator to a 391 km x 63452 km x 24.8 deg orbit. The two payloads were 2000 kg Boeing BSS-702SP models with XIPS-25 ion thrusters as their main propulsion system. ABS-3A, for Asia Broadcast Satellite of Hong Kong, was launched directly attached to the lower satellite, Eutelsat 115 West B, until it separated from the stack following stage 2 second cutoff.
- Eutel.115 West B - . Payload: BSS-702SP. Mass: 2,000 kg (4,400 lb). Nation: Mexico. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 40425 . COSPAR: 2015-010B. Apogee: 35,787 km (22,236 mi). Perigee: 35,786 km (22,236 mi). Inclination: 0.00 deg. Period: 1,436.10 min. Eutelsat 115 West B was owned by Eutelsat Americas (Mexico City), and was called Satmex 7. Satmex was taken over by Europe's Eutelsat and renamed Eutelsat Americas in March 2014..
2015 May 16 - . 05:47 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M. FAILURE: Malfunction of the third stage vernier engine 8 minutes into flight led to a premature shutdown and impact of stage 3, Briz-M and payload in the Chita region between Lake Baikal and the Chinese border.. Failed Stage: 3.
- Mexsat-1 - . Payload: Boeing 702-GEM. Mass: 5,325 kg (11,739 lb). Nation: Mexico. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. Apogee: 160 km (90 mi). Perigee: -2,000 km (-2,000 mi). Inclination: 50.50 deg. Satellite for the Mexican Communications Ministry, providing secure military communications and enhanced civilian services..
2015 July 24 - . 00:07 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC37B. LV Family: Delta IV. Launch Vehicle: Delta 4M+(5,4).
- USA 263 - .
Payload: WGS 7. Mass: 6,200 kg (13,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 40746 . COSPAR: 2015-036A. Apogee: 66,798 km (41,506 mi). Perigee: 494 km (306 mi). Inclination: 24.10 deg.
Wideband Global Satcom military communications satellite launched initially into a supersynchronous geotransfer orbit. WGS satellites were managed by the USAF Space and Missile Center and replaced the older DSCS system with X-band and Ka-band communications systems. Second Delta 4 launch to use the uprated RS-68A main engine.
2015 August 28 - . 11:44 GMT - . Launch Site: Baikonur. Launch Complex: Baikonur LC200/39. Launch Pad: Baikonur LC200. LV Family: Proton. Launch Vehicle: Proton-M/Briz-M.
- Inmarsat 5 F3 - . Payload: Boeing 702HP. Mass: 6,100 kg (13,400 lb). Nation: International. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 40882 . COSPAR: 2015-042A. Apogee: 35,792 km (22,240 mi). Perigee: 35,779 km (22,231 mi). Inclination: 0.0500 deg. Period: 1,436.05 min. First Proton flight since the launch failure in May. Communications satellite providing roadband mobile communications services with 89 Ka-band transponders..
2015 October 2 - . 10:28 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC41. LV Family: Atlas V. Launch Vehicle: Atlas V 421.
- Morelos-3 - . Payload: Boeing 702HP GeoMobile. Mass: 5,400 kg (11,900 lb). Nation: Mexico. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 40946 . COSPAR: 2015-056A. Apogee: 35,790 km (22,230 mi). Perigee: 35,783 km (22,234 mi). Inclination: 7.09 deg. Period: 1,436.09 min. Mexican communications satellite with a 22-metre L-band antenna reflector..
2016 January 27 - . 23:20 GMT - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA3. LV Family: Ariane 5. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 5ECA.
- Intelsat IS-29e - .
Nation: Europe.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 41308 . COSPAR: 2016-004A. Apogee: 35,525 km (22,074 mi). Perigee: 280 km (170 mi). Inclination: 0.60 deg.
Intelsat communications satellite in a low-inclination geotransfer orbit; carried C, Ku and Ka-band communications payload and was the first of Intelsat's new broadband high-throughput 'Epic-NG' series, built by Boeing using the BSS-702MP bus. Launch mass was 6552 kg.
2016 June 15 - . 14:29 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC40. Launch Pad: Cape Canaveral SLC40. LV Family: Falcon. Launch Vehicle: Falcon 9 v1.2.
- Eutelsat 117 West B - . Nation: USA. Class: Communications. Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702. USAF Sat Cat: 41589 . COSPAR: 2016-038B. Apogee: 62,761 km (38,997 mi). Perigee: 399 km (247 mi). Inclination: 24.70 deg. Eutelsat 117 West B (the former Satmex 9) to provide service for Eutelsat Americas, supplementing Satmex 8 (now renamed Eutelsat 117 West A). Boeing BSS-702SP satellite with all-electric-propulsion, which use ion engines to complete the trip to GEO..
- ABS-2A - .
Nation: USA.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 41588 . COSPAR: 2016-038A. Apogee: 62,649 km (38,928 mi). Perigee: 395 km (245 mi). Inclination: 24.60 deg.
The Falcon 9 vehicle 26 second stage made two burns to deliver a pair of Boeing BSS-702SP satellites to supersynchronous transfer orbits. This was the second matched pair of all-electric-propulsion payloads, which use ion engines to complete the trip to GEO. ABS-2A will supplement Asia Broadcast Satellite's ABS-2
2016 August 24 - . 22:16 GMT - . Launch Site: Kourou. Launch Complex: Kourou ELA3. LV Family: Ariane 5. Launch Vehicle: Ariane 5ECA.
- Intelsat IS-33e - .
Nation: Europe.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 41748 . COSPAR: 2016-053B. Apogee: 35,804 km (22,247 mi). Perigee: 15,756 km (9,790 mi). Inclination: 0.60 deg.
Second Epic high throughput broadband satellite, a Boeing BSS-702MP model. Suffered suffered a failure of its main Leros apogee thruster in geotransfer orbit. Orbit raising was delayed until late September; by Oct 18 the satellite was in a 31428 x 35927 km x 0.1 deg orbit.
2016 December 7 - . 23:52 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC37B. Launch Pad: Cape Canaveral SLC37B. LV Family: Delta IV. Launch Vehicle: Delta 4M+(5,4).
- USA 272 - .
Payload: WGS 8 / WGS SV-8. Mass: 6,200 kg (13,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 41879 . COSPAR: 2016-075A. Apogee: 44,207 km (27,468 mi). Perigee: 430 km (260 mi). Inclination: 27.00 deg.
8th Boeing 702-class Wideband Global Satcom payload for the US Dept. of Defense carried an improved 'channelizer' that increases the capacity of the satellite. The second stage was reportedly deorbited, and the extra propellant required to do this necessitated a lower apogee transfer orbit than for previous WGS missions. By Dec 25 WGS-8 had reached a 26728 x 44588 km x 0.2 deg orbit.
2017 March 19 - . 00:18 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC37B. Launch Pad: Cape Canaveral SLC37B. LV Family: Delta IV. Launch Vehicle: Delta 4M+(5,4).
- USA 275 - .
Payload: WGS 9. Mass: 6,200 kg (13,600 lb). Nation: USA.
Class: Communications.
Type: Communications satellite. Spacecraft: HS 702.
USAF Sat Cat: 42075 . COSPAR: 2017-016A. Apogee: 44,262 km (27,503 mi). Perigee: 430 km (260 mi). Inclination: 27.00 deg.
See WGS 9 (USA 275). Wideband Global Satcom 9 was to be added to the US DoD communications satellite constellation. This WGS was partly funded by allied countries, although it was still owned and operated by USAF. A United Launch Alliance Delta 4 sent the satellite aloft on Mar 19, first into a 185 x 6097 km x 27.6 deg parking orbit and then to a 430 x 44262 km x 27.0 deg supersynchronous transfer orbit. The Delta 377 second stage was deorbited over the Pacific near the Phillipines with reentry around 1230 UTC.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use