
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
STS-8

STS-8
Crew compartment flight deck window debris, damage, streak documentation
Credit: NASA
AKA: Challenger. Launched: 1983-08-30. Returned: 1983-09-05. Number crew: 5 . Duration: 6.05 days.
First night launch and night landing. Deployed Insat 1B. Payloads: Deployment of INSAT (India communication satellite) with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D, Payload Flight Test Article (PFTA)/ Payload Deployment Retrieval System (PDRS), Continuous Flow Electrophoresis (CFES), biomedical experiments. 250,000 express mail envelopes with special cachet for U.S. Postal Service were carried for a first-day cover.
Orbits of Earth: 97. Distance traveled: 4,046,660 km. Orbiter Liftoff Mass: 110,105 kg. Orbiter Mass at Landing: 92,506 kg. Payload to Orbit: 13,642 kg. Payload Returned: 10,265 kg. Landed at: Concrete runway 22 at Edwards Air Force Base, Cali. Landing Speed: 361 kph. Touchdown miss distance: 851 m. Landing Rollout: 2,856 m.
NASA Official Mission Narrative
Mission Name: STS-8 (8)
CHALLENGER (3)
Pad 39-A (20)
8th Shuttle mission
3rd Flight OV-099
1st Night Launch
1st Night Landing
Crew:
Richard H. Truly (2), Commander
Daniel C. Brandenstein (1), Pilot
Dale A. Gardner (1), Mission Specialist
Guion S. Bluford (1), Jr., Mission Specialist
William E. Thornton (1), Mission Specialist
Milestones:
OPF - June 3O, 1983
VAB - July 26, 1983
PAD - Aug. 2, 1983
Payload:
INSAT-1B,PDRS/PFTA,CFES(4),OIM,MLR(3),GAS(x7)
Mission Objectives:
Launch:
August 30, 1983, 2:32:00 a.m. EDT. Launch delayed 17 mlnutes due to weather. Launch Weight: 242,742 lbs.
Orbit:
Altitude: 191nm
Inclination: 28.5 degrees
Orbits: 98
Duration: Six days, one hour, eight minutes, 43 seconds.
Distance: 2,514,478 miles
Hardware:
SRB: BI-008
SRM: 008LW(HPM)
ET : 9/LWT-2
MLP : 2
SSME-1: SN-2017
SSME-2: SN-2015
SSME-3: SN-2012
Landing:
September 5,1983, 12:40:43 a.m. PDT, Runway 22, Edwards Air Force Base, Calif. Rollout distance: 9,371 feet. Rollout time: 50 seconds. Orbiter returned to KSC Sept. 9, 1983. Landing Weight 203,945 lbs
Mission Highlights:
Bluford became first African-American to fly in space. INSAT-1B, a multipurpose satellite for India attached to Payload Assist Module-D (PAM-D) motor, was deployed. Nose of orbiter held away from sun 14 hours to test flight deck area in extreme cold. For Development Flight Instrumentation Pallet (DFI PLT), crew filmed performance of experimental heat pipe mounted in cargo bay; also, orbiter dropped to 139 miles altitude to perform tests on thin atomic oxygen to identify cause of glow that surrounds parts of orbiter at night. Remote manipulator system tested to evaluate joint reactions to higher loads. Biofeedback experiments: six rats flown in Animal Enclosure Module to observe animal reactions in space. Other payloads: Continuous Flow Electrophoresis System (CFES); Shuttle Student Involvement Program (SSlP) experiment; Incubator-Cell Attachment Test (l CAT); Investigation of STS Atmospheric Luminosities (ISAL); Radiation Monitoring Equipment (RME); and five Get Away Special experiment packages including eight cans of postal covers. Testing conducted between Tracking and Data Relay Satellite-I (TDRS-1 ) and orbiter using Ku-band antenna, and investigations continued on Space Adaptation Syndrome.
More at: STS-8.
Family: Manned spaceflight. People: Bluford, Brandenstein, Gardner, Thornton, Bill, Truly. Country: USA. Spacecraft: Challenger. Projects: STS. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral. Agency: NASA, NASA Houston.
 | STS-8 Credit: www.spacefacts.de |
 | STS-8 Mission Specialist (MS) Bluford exercises on middeck treadmill Credit: NASA |
 | STS-8 Aft flight deck documentation with free floating headset interface unit (HIU) Credit: NASA |
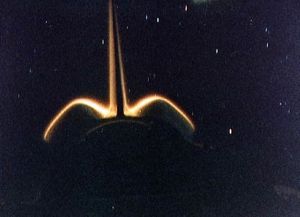 | STS-8 ISAL experiment documentation of vertical tail and OMS pods Credit: NASA |
 | STS-8 Close up view of the PFTA being lifted out of the payload bay Credit: NASA |
 | STS-8 View of the INSAT/PAM-D being deployed Credit: NASA |
1983 August 30 - . 06:32 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC39A. Launch Platform: MLP2. LV Family: Shuttle. Launch Vehicle: Space Shuttle.
- STS-8 - .
Call Sign: Challenger. Crew: Bluford,
Brandenstein,
Gardner,
Thornton, Bill,
Truly.
Payload: Challenger F03 / PFTA. Mass: 13,642 kg (30,075 lb). Nation: USA.
Related Persons: Bluford,
Brandenstein,
Gardner,
Thornton, Bill,
Truly.
Agency: NASA Houston.
Program: STS.
Class: Manned.
Type: Manned spaceplane. Flight: STS-8.
Spacecraft Bus: Shuttle.
Spacecraft: Challenger.
Duration: 6.05 days. Decay Date: 1983-09-05 . USAF Sat Cat: 14312 . COSPAR: 1983-089A. Apogee: 313 km (194 mi). Perigee: 306 km (190 mi). Inclination: 28.50 deg. Period: 90.70 min.
First night launch and night landing. Deployed Insat 1B. Payloads: Deployment of INSAT (lndia communica-tion satellite) with Payload Assist Module (PAM)-D, Payload Flight Test Article (PFTA)/ Payload Deployment Retrieval System (PDRS), Continuous Flow Electrophoresis (CFES), biomedical experiments. 250,000 express mail envelopes with special cachet for U.S. Postal Service were carried for a first-day cover.
1983 August 31 - .
- STS-8 - Wakeup Song: Georgia Tech Fight Song - . Flight: STS-8. "Georgia Tech Fight Song" for the alma mater of Commander Richard Truly..
1983 September 1 - .
- STS-8 - Wakeup Song: Illinois Fight Song - . Flight: STS-8. "Illinois Fight Song" for Mission Specialist Dale Gardner's alma mater..
1983 September 2 - .
- STS-8 - Wakeup Song: Penn State Fight Song - . Flight: STS-8. "Penn State Fight Song" for Guy Bluford's Alma Mater.
1983 September 3 - .
- STS-8 - Wakeup Song: University of North Carolina Fight Song - . Flight: STS-8. "University of North Carolina Fight Song" for alumnus Bill Thornton..
1983 September 4 - .
- STS-8 - Wakeup Song: Tala Sawari - . Flight: STS-8. "Tala Sawari" performed by sitar player Ravi Shankar in honor of release of Indian INSAT satellite..
1983 September 5 - .
- STS-8 - Wakeup Song: Semper Fidelis - . Flight: STS-8. "Semper Fidelis" by John Philip Sousa. CAPCOM Brian O'Connor was a Marine Corps officer..
1983 September 5 - .
- Landing of STS-8 - . Return Crew: Bluford, Brandenstein, Gardner, Thornton, Bill, Truly. Nation: USA. Related Persons: Bluford, Brandenstein, Gardner, Thornton, Bill, Truly. Program: STS. Flight: STS-8. STS-8 landed at 07:40 GMT. .
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use