
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
Vela
 Vela Credit: USAF |
Status: Operational 1963. First Launch: 1963-10-17. Last Launch: 1965-07-20. Number: 6 . Gross mass: 225 kg (496 lb). Height: 1.40 m (4.50 ft).
The Vela Nuclear Detection Satellites were launched in pairs into high altitude orbits to detect possible nuclear explosions in space and on earth.
The project was directed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency of the Department of Defense; the USAF Space and Missile Systems organization was responsible for the development of the-spacecraft. Prime Contractor was TRW Systems Group of TRW Inc. The first pair of satellites was launched in October 1963, the second in July 1964, and the third in July 1965. The satellites were so successful, each operating for at least 5 years, that a planned acquisition of a fourth and fifth set of pairs was cancelled. Instead, TRW was awarded a further contract in March 1965 for an Advanced Vela spacecraft series. The Vela series was the first spacecraft procurement to utilize a fixed price incentive contract.
The spacecraft was spin stabilized at 120 rpm. The 20-sided polyhedron had body mounted solar cells generating 90 W. During launch, 2 satellites were connected by a central cylinder containing an apogee motor. The payload included twelve external X-ray detectors and 18 internal neutron and gamma-ray detectors. The third pair of satellites (F5, 6) carried an improved detector package, including an optical nuclear flash instrument.
NASA NSSDC Master Catalog Description
Vela 5B was one of two spin-stabilized, polyhedral satellites that comprised the fifth launch in the Vela program. The orbits of the two satellites on each launch were basically circular at about 17 earth radii, inclined at 60 deg to the ecliptic, and spaced 180 deg apart, thus providing a capability of monitoring opposite sides of the earth. The objectives of the satellites were (1) to study solar and cosmic X rays, extreme ultraviolet radiation (EUV), solar protons, solar wind, and neutrons, (2) to carry out research and development on methods of detecting nuclear explosions by means of satellite-borne instrumentation, and (3) to provide solar flare data in support of manned space missions. Vela 5B, an improved version of the earlier Vela series satellites, had better command capabilities, increased data storage, improved power requirements, better thermal control of optical sensors, and greater experimentation weight. Power supplies of 120 W were provided by 22,500 solar cells mounted on 24 of the spacecraft's 26 faces. A rotation rate of 78 rpm during transfer orbits and 1 rpm after final orbit insertion maintained nominal attitude control. Eight whip antennas and four stub antenna arrays at opposite ends of the spacecraft structure were used for ground command and telemetry.
More at: Vela.
| Vela 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 (advanced Vela) Null |
Family: High earth orbit, Nuclear detection surveillance satellite, Surveillance. Country: USA. Launch Vehicles: Atlas, Atlas Agena D. Launch Sites: Cape Canaveral, Cape Canaveral LC13. Agency: USAF, TRW. Bibliography: 2, 278, 279, 6, 7014, 13328.
 | Vela 1 Credit: Manufacturer Image |
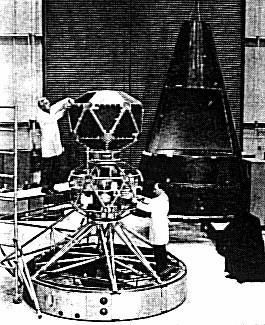 | Vela prepared Vela prepared for launch Credit: USAF |
1959 October 6 - .
- Vela Hotel development plan - . Spacecraft: Vela. As a result of Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) tasking of 18 September, AFBMD issued an abbreviated Vela Hotel development plan for a system to detect and locate nuclear detonations in space..
1960 December 15 - .
- Vela Hotel begun. - .
Spacecraft: Vela.
The Vela Hotel Joint Management Team, with representatives from ARDC, NASA, and the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC), met at AFBMD headquarters. They began planning a high-altitude satellite system that would be capable of detecting nuclear explosions on the Earth's surface or in space.
1961 Sep - .
- Vela nuclear detection satellite contractor selection. - . Spacecraft: Vela. Space Systems Division selected Space Technology Laboratories (STL) as the contractor to build the spacecraft for the Vela nuclear detection satellite program..
1961 November 24 - .
- Vela satellite system for detection of nuclear detonations on Earth or in space. - . Spacecraft: Vela. ARPA selected Space Technology Laboratories to develop the Vela satellite system for detection of nuclear detonations on Earth or in space..
1963 October 17 - . 02:37 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- Vela 2 - .
Payload: Vela 1B. Mass: 220 kg (480 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela.
USAF Sat Cat: 674 . COSPAR: 1963-039A. Apogee: 116,582 km (72,440 mi). Perigee: 101,081 km (62,808 mi). Inclination: 38.70 deg. Period: 6,486.20 min.
Space Systems Division, acting.as program manager for the Defense Department, launched two Vela nuclear radiation detection satellites from Cape Canaveral aboard the first Atlas D/Agena D (SLV-3/SS-01A) launch vehicle (197D). The Vela satellites were developed and produced by the TRW Systems and were the first pair in a series of satellites designed to provide information on nuclear detonations in the atmosphere or in outer space to a distance of 100 million miles. The 297-pound satellites were placed in near-circular orbits approximately 70,000 miles above the Earth's surface. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- Vela 1 - . Payload: Vela 1A. Mass: 220 kg (480 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela. USAF Sat Cat: 692 . COSPAR: 1963-039C. Apogee: 116,528 km (72,407 mi). Perigee: 101,925 km (63,333 mi). Inclination: 37.80 deg. Period: 6,519.60 min. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1964 July 17 - . 08:22 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- Vela 3 - .
Payload: Vela 2A / OPS 3662. Mass: 220 kg (480 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela.
USAF Sat Cat: 836 . COSPAR: 1964-040A. Apogee: 104,101 km (64,685 mi). Perigee: 102,500 km (63,600 mi). Inclination: 39.10 deg. Period: 6,024.80 min.
An Atlas D/Agena D launch vehicle (Atlas 216D), carrying the second set of Vela Nuclear Detection Satellites, was launched from Cape Canaveral and placed the satellites in their prescribed orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
- Vela 4 - .
Payload: Vela 2B / OPS 3674. Mass: 220 kg (480 lb). Nation: USA.
Agency: USAF.
Class: Surveillance.
Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela.
USAF Sat Cat: 837 . COSPAR: 1964-040B. Apogee: 114,000 km (70,000 mi). Perigee: 92,103 km (57,230 mi). Inclination: 40.80 deg. Period: 6,004.30 min.
An Atlas D/Agena D launch vehicle (Atlas 216D), carrying the second set of Vela Nuclear Detection Satellites, was launched from Cape Canaveral and placed the satellites in their prescribed orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A).
1965 July 20 - . 08:27 GMT - . Launch Site: Cape Canaveral. Launch Complex: Cape Canaveral LC13. LV Family: Atlas. Launch Vehicle: Atlas Agena D.
- Vela 5 - . Payload: Vela 3A / OPS 6577. Mass: 235 kg (518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela. USAF Sat Cat: 1458 . COSPAR: 1965-058A. Apogee: 115,839 km (71,978 mi). Perigee: 106,367 km (66,093 mi). Inclination: 35.20 deg. Period: 6,679.00 min. Air Force Atlas/Agena D lifted the third pair of Vela nuclear detection satellites into their 70,000-mile, nearly circular orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
- Vela 6 - . Payload: Vela 3B / OPS 6564. Mass: 235 kg (518 lb). Nation: USA. Agency: USAF. Class: Surveillance. Type: Nuclear detection surveillance satellite. Spacecraft: Vela. USAF Sat Cat: 1459 . COSPAR: 1965-058B. Apogee: 121,281 km (75,360 mi). Perigee: 101,715 km (63,202 mi). Inclination: 34.20 deg. Period: 6,712.70 min. An Air Force Atlas/Agena D lifted the third pair of Vela nuclear detection satellites into their 70,000-mile, nearly circular orbits. Space craft engaged in investigation of spaceflight techniques and technology (US Cat A)..
1975 July 1 - .
- SAMSO's responsibility for the Vela Program came to an end. - . Spacecraft: Vela.
Back to top of page
Home - Search - Browse - Alphabetic Index: 0- 1- 2- 3- 4- 5- 6- 7- 8- 9
A- B- C- D- E- F- G- H- I- J- K- L- M- N- O- P- Q- R- S- T- U- V- W- X- Y- Z
© 1997-2019 Mark Wade - Contact
© / Conditions for Use